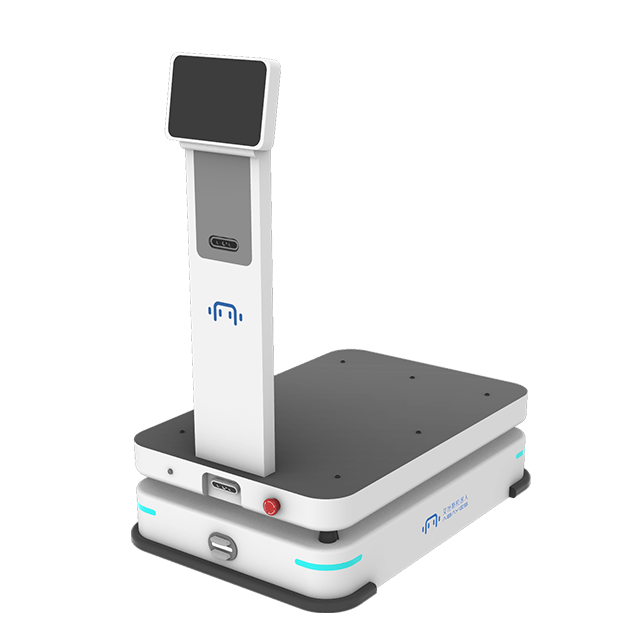
Pain points in the scenario:
3C electronic factories typically have complex production lines and warehouses, with large workshop areas and scattered distribution of production parts. This complexity makes traditional manual handling prone to errors, leading to damaged or lost items. Moreover, 3C electronic products come in a variety of types, and some are sensitive to electrostatic discharge and dust, requiring special handling. Manual handling is not suitable for such scenarios. Furthermore, the efficiency of production lines is constrained by the speed and accuracy of manual handling, impacting production capacity and delivery schedules. Additionally, repetitive labor and high-intensity work can result in employee health issues and high turnover rates.
Implementation Challenges:
The introduction of material handling robots in 3C electronic factories involves the following challenges:
- Site Planning: It requires a rational layout planning of the factory to ensure that robots can move smoothly and complete tasks.
- Level of Automation: Achieving a high level of automation for robots, including autonomous navigation, task scheduling, and anomaly handling. In complex production line and warehouse environments, robots need to possess intelligent perception and obstacle avoidance capabilities to ensure safe operation.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration of materialhandling robots with existing production systems and equipment is essential to achieve real-time updates of logistics information and optimize scheduling, ensuring coordinated operations.
Solutions:
- Task Assignment: The production system assigns handling tasks to robots based on production plans and logistics requirements.
- Autonomous Navigation: Robots autonomously plan optimal paths within the factory using navigation technologies like lasers and vision, depending on task requirements.
- Handling Actions: Robots use mechanical arms and other devices to complete the handling tasks.
- Anomaly Handling: In the event of obstacles or other anomalies, robots can sense and take appropriate actions, such as navigating around obstacles or requesting assistance, through sensors.
- Task Completion Reporting: After completing tasks, robots submit task completion reports to the system for updating task status and data analysis.
Highlights of the Solution:
- Improved Efficiency: Automated materialhandling significantly enhances production efficiency by reducing handling time and optimizing production processes.
- Cost Reduction: Reduced human resource input lowers labor costs and minimizes errors and losses caused by human operations.
- Flexibility: Robots can flexibly adjust work tasks and optimize paths according to production plans, adapting to varying production demands.
- Safety: The solution reduces safety hazards associated with manual handling, ensuring employee health and safety.
- Data-Driven Management: Robots can record and upload data during the handling process, helping manufacturers with data analysis and process optimization.